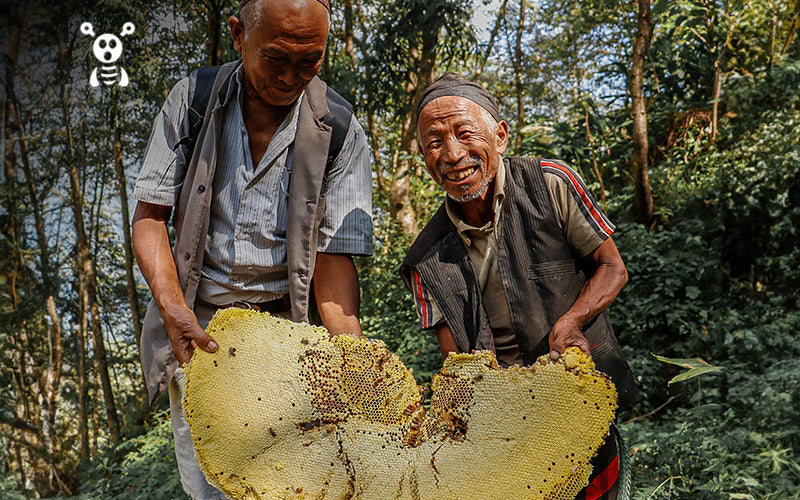
Hidden within the rugged terrains of Nepal and the Himalayas lies a rare gem – mad honey. This exquisite honey, crafted by bees from the nectar of rhododendron flowers, has captivated adventurers and health enthusiasts for generations. Due to the increased interest in natural remedies, mad honey has gained prominence for its distinct flavor and alleged medicinal properties. Still, the journey from hive to market is not without challenges. Issues ranging from ethical dilemmas surrounding bee welfare to regulatory hurdles regarding consumer safety have made the trade a complex landscape. Join us as we unravel the mysteries of this unique industry, examining its origins, dynamics, and the debates shaping its future.
What is Mad Honey?
Mad honey, also known as hallucinogenic honey, is produced by bees that collect nectar from rhododendron flowers. These flowers contain grayanotoxins, which give mad honey its unique properties. Consuming mad honey can lead to a range of effects, from mild intoxication and euphoria to hallucinations and even more severe symptoms if taken in large quantities. The honey's distinctiveness has made it a sought-after substance, despite the potential risks associated with its consumption.Part 1: The Origins of Mad Honey
1.1 Historical Significance
Mad honey has a storied history, particularly in the regions where it is harvested. In Nepal, the practice of collecting mad honey dates back centuries and is deeply intertwined with local culture and traditions. The honey hunters of Nepal, known for their daring cliffside collections, have passed down their techniques through generations and have traditionally used the honey in rituals and as a natural remedy for various ailments.1.2 The Honey Hunting Process
The process of collecting mad honey is not for the faint-hearted. Honey hunters climb steep cliffs to reach the hives of the Himalayan giant bees. Equipped with minimal gear and immense bravery, they smoke out the bees to calm them before carefully extracting the honeycombs. This method, while risky, guarantees the purity of the honey and respects the natural habitat of the bees.

Part 2: Benefits and Legality of Mad Honey
2.1 Therapeutic Benefits of Mad Honey
Mad honey has long been valued for its medicinal benefits. From ancient cultures to modern therapeutic applications, this extraordinary honey offers a range of health advantages. However, its potency necessitates careful consumption and awareness of its potential side effects.2.1.1 Historical Use in Traditional Medicine
Mad honey has a rich heritage in traditional medicine, particularly in regions like Nepal and Turkey, where it has been used for centuries to treat various ailments. Traditional healers prized mad honey for its soothing properties and its effectiveness in treating respiratory conditions. For instance, mad honey was commonly used to alleviate symptoms of bronchitis and asthma. Its anti-inflammatory properties helped reduce airway inflammation, making it easier for patients to breathe. Moreover, mad honey's soothing texture made it a popular home remedy for coughs and sore throats. It is believed to coat the throat, providing a protective layer that alleviates irritation and has antibacterial properties to combat infections.2.1.2 Scientifically Recognised Health Benefits
Recent scientific studies have begun to validate many of the traditional claims about mad honey, revealing a host of potential health benefits. One significant benefit is its high antioxidant content. Mad honey is rich in antioxidants, which help neutralize harmful free radicals in the body. This can reduce oxidative stress and lower the risk of chronic diseases such as cancer and coronary artery disease. Additionally, the honey's antiradical properties further support its potential in preventing cancer and other degenerative diseases. Its antimicrobial effects make it effective in combating infections, supporting the immune system, and promoting overall health.
Furthermore, mad honey's anti-inflammatory properties are beneficial in treating various inflammatory disorders. By reducing inflammation, it can help manage conditions like arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease. The combined antioxidant and anti-inflammatory abilities of mad honey are believed to combat the signs of aging, promoting healthier, more youthful skin and reducing the risk of age-related diseases.
2.1.3 Mad Honey in Modern Therapeutics
In contemporary medicine, mad honey is being explored for its potential in treating a variety of conditions, highlighting its versatility and effectiveness. For example, mad honey is considered an alternative treatment for gastrointestinal issues, including ulcers and gastritis. Its soothing properties help protect the stomach lining, while its antimicrobial capabilities combat harmful bacteria. Some studies suggest that mad honey can positively impact heart health by helping to regulate blood pressure levels, making it a potential natural remedy for hypertension.
Beyond traditional uses for bronchitis and asthma, modern research supports mad honey's effectiveness in treating a range of respiratory conditions. Its ability to reduce inflammation and soothe irritated tissues makes it beneficial for patients with chronic coughs and other respiratory ailments. Additionally, while more anecdotal, some believe that mad honey acts as an aphrodisiac, enhancing libido and sexual performance. This aspect of mad honey is still under investigation but remains a point of interest in natural medicine.
2.1.4 Precautions and Recommended Dosage
Despite its many benefits, mad honey must be consumed with caution due to its potent properties. It is generally recommended to consume no more than 1 to 3 teaspoons of mad honey per day. This amount is considered safe for most individuals and is unlikely to cause adverse effects. However, the potency of mad honey can vary based on individual factors such as body weight, metabolism, and overall health. People with lower body weight or sensitive constitutions should start with smaller doses to gauge their reaction. Overconsumption of mad honey can lead to several side effects, including severe nausea, vomiting, dizziness, blurred vision, sweating, and increased blood pressure. In rare cases, it can cause more severe symptoms such as irregular heartbeat, temporary paralysis, and unconsciousness.
Additionally, mad honey is known for its psychotropic capabilities, which can occur within 20 minutes of consumption and last up to 3 to 5 hours. These can include hallucinations, euphoria, and altered perception. The after-effects may persist for up to 24 hours. Therefore, new users are advised to start with lower doses of mad honey to assess their tolerance. This cautious approach helps prevent severe reactions and allows individuals to enjoy the benefits of mad honey safely.
2.2 Legal Status and Safety Guidelines
Mad honey's unique properties and potency have necessitated a complex legal and regulatory landscape. Understanding the legality, safety precautions, and stringent regulations surrounding mad honey is crucial for consumers and traders alike.2.2.1 Legal Landscape
The legality of mad honey varies significantly across different regions of the world. In the United States, Europe, and the United Kingdom, mad honey is legally available for purchase. These regions have established regulations to ensure the product's safety and quality, allowing consumers to enjoy mad honey without undue risk. However, in several other countries, mad honey is banned due to its potent properties and potential health risks. Countries such as South Korea, Australia, and Brazil have prohibited the sale and distribution of mad honey. These bans are primarily driven by concerns over grayanotoxin, the active compound in mad honey, which can cause severe adverse reactions if consumed in excess. The strict regulations in countries where mad honey is legal are designed to mitigate these risks, making sure that only safe, properly labeled products reach the market.2.2.2 Safety Precautions
The primary active ingredient in mad honey, grayanotoxin, is responsible for its uniqueness and potency. However, grayanotoxin can also cause a range of side effects if consumed excessively. Mild side effects of grayanotoxin include dizziness, nausea, blurred vision, and a drop in blood pressure. These symptoms can be uncomfortable but are generally not life-threatening. In more severe cases, overconsumption of mad honey can lead to vomiting, irregular heartbeat, temporary paralysis, blue-tinged skin, seizures, and even unconsciousness. These severe reactions underscore the importance of consuming mad honey responsibly and adhering to recommended dosages.
To safeguard yourself when consuming mad honey, it is important to follow several guidelines. First, always purchase mad honey from reputable sources. This helps certify that the product is genuine and meets safety standards. Second, check for proper labeling on mad honey products. Proper labeling should provide information about the honey's origin, ingredients, potential risks, and recommended usage conditions. Finally, limit your intake of mad honey to avoid adverse reactions. If you experience any adverse symptoms after consuming mad honey, seek medical attention immediately.
2.2.3 Regulations and Labeling
In regions where mad honey is legal, regulatory bodies have established specific guidelines to govern its production, labeling, and sale. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a pivotal role in regulating mad honey. The FDA's regulations validate that mad honey products meet stringent safety and quality standards. Producers must adhere to these guidelines, which include proper labeling and packaging requirements. This helps consumers make informed decisions and reduces the risk of adverse reactions.
Similarly, in Europe, mad honey must comply with the regulations set forth by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). The EFSA's regulations cover various aspects of mad honey production and labeling to make certain that products are safe for consumption. Labeling standards in Europe require accurate information about the product's ingredients, potential risks, and intended conditions of use. This transparency helps consumers understand what they are purchasing and how to use it safely.
In both the United States and Europe, these regulatory measures aim to protect consumers while allowing them to enjoy the unique benefits of mad honey. Compliance with these regulations is paramount for producers and traders to prove that their products are safe, properly labeled, and legally marketable.

Part 3: A Look at the Commercial Side of Things
3.1 Ethical Dimensions of Mad Honey
The trade and consumption of mad honey cover several ethical considerations that go beyond mere economic transactions. These ethical dimensions involve environmental sustainability, cultural sensitivity, community engagement, and the need for transparency and accountability.3.1.1 Environmental Impact
The extensive harvesting of mad honey has significant implications for local ecosystems. Rhododendron flowers, which are the primary source of mad honey, play a vital role in maintaining ecological balance. These flowers provide the necessary nectar for various insects and animals, supporting a diverse range of species. Overharvesting of the flowers for mad honey production can lead to a reduction in their availability, disrupting the food chain and affecting the biodiversity of the region. This disruption can cause imbalances in local ecosystems, impacting flora and fauna that rely on these flowers for sustenance. The environmental impact of mad honey harvesting therefore requires careful management to ensure that these ecosystems remain healthy and vibrant. Sustainable harvesting practices are required to mitigate these negative consequences and maintain the ecological integrity of the regions where mad honey is produced.3.1.2 Cultural Sensitivity
Respecting the cultural heritage and practices of indigenous communities is indispensable in the mad honey trade. Indigenous communities in regions such as Nepal have a deep cultural connection to mad honey, which they have used for centuries in traditional rituals and medicinal practices. These communities view mad honey as an integral part of their cultural identity and heritage. Commercial exploitation of mad honey without proper consultation and respect for these traditions can lead to cultural appropriation and disenfranchisement. It is essential to engage in fair and equitable partnerships with indigenous communities, taking care that their knowledge and practices are respected and preserved. By involving these communities in decision-making processes and recognizing their contributions, the mad honey trade can support the preservation of cultural heritage while promoting sustainable economic development.3.1.3 Community Engagement
Engaging and empowering local communities involved in mad honey production is vital for the ethical sustainability of the trade. These communities should receive fair compensation for their labor and the traditional knowledge they contribute to honey production. Fair compensation not only provides immediate financial benefits but also supports the long-term well-being of these communities. The mad honey trade has the potential to support sustainable development by providing income diversification and creating employment opportunities in rural areas. Supporting initiatives that promote sustainable beekeeping practices and community empowerment is urgent so that the benefits of mad honey production are equitably distributed. This includes investing in community development projects, educational programs, and infrastructure improvements that enhance the quality of life for local populations.3.1.4 Transparency and Accountability
Transparency and accountability are fundamental to maintaining consumer trust and guaranteeing the ethical integrity of mad honey products. Proper labeling and certification of mad honey products are essential for consumer safety and transparency. Labels should include detailed information on the origin of the honey, production methods, and potential risks associated with its consumption. This information helps consumers make informed decisions and verifies that they are aware of any health considerations. Producers and traders involved in the mad honey trade must adhere to ethical practices, including compliance with quality standards and regulatory requirements. This involves regular monitoring and auditing of production processes to certify that they meet established guidelines. By upholding these standards, producers and traders can build consumer confidence and maintain the credibility of mad honey products in the market.3.2 The Business Dynamics of Mad Honey
Understanding the business dynamics of mad honey involves a comprehensive analysis of the market, production processes, marketing strategies, regulatory frameworks, economic impacts, and future outlook. These elements collectively shape the success and sustainability of mad honey as a unique and valuable product in the global market.3.2.1 Market Analysis
To effectively tap into the mad honey market, it is essential to analyze current consumer demand by examining preferences, health trends, and cultural influences. This involves conducting market research to quantify the market size, growth potential, and consumer behavior patterns. Understanding these dynamics helps identify opportunities for market expansion and differentiation. Competitor analysis plays a critical role in formulating effective marketing and positioning strategies. Through assessing the product offerings, pricing strategies, distribution channels, and market shares of key players, businesses can develop competitive advantages and tailor their strategies to meet market needs.3.2.2 Production and Supply Chain
The production of mad honey involves a series of intricate steps, starting with bee foraging and nectar collection. Bees collect nectar from rhododendron flowers, which is then processed into honey. This raw honey undergoes extraction, filtration, and packaging before reaching the market. The supply chain includes various stakeholders, like beekeepers, processors, distributors, and retailers. Evaluating the efficiency and sustainability of this supply chain is crucial for identifying areas for improvement. Improving supply chain operations can reduce costs, increase product quality, and ensure the reliability of supply. Sustainability practices, such as ethical sourcing and environmentally friendly production methods, also play a significant role in maintaining the ecological balance and long-term viability of the trade.3.2.3 Marketing Strategies
Effective marketing strategies for mad honey require identifying target demographic segments based on consumer preferences, lifestyle choices, and health concerns. These segments might include health-conscious consumers, culinary enthusiasts, and individuals interested in traditional medicine. Marketing messages should resonate with these niche markets by highlighting the unique attributes of mad honey, such as its distinct flavor, medicinal properties, and cultural heritage. Creating a compelling brand story around these aspects can enhance consumer engagement and loyalty. Digital marketing channels, like social media, email marketing, and influencer partnerships, offer powerful tools for reaching and engaging target audiences. Visual content, educational materials, and testimonials can further strengthen the brand's appeal and credibility.3.2.4 Regulatory Considerations
Compliance with relevant regulations governing food safety, labeling, packaging, and marketing is critical for the mad honey business. Understanding the regulatory requirements in different jurisdictions helps businesses avoid legal issues and penalties. This includes adhering to guidelines set by food safety authorities such as the FDA in the United States or the EFSA in Europe. Obtaining certifications, such as organic, fair trade, or geographical indication (GI), strengthens the credibility and marketability of mad honey products. These certifications provide assurance to consumers about the quality, authenticity, and ethical production practices of the honey, fostering trust and increasing demand.3.2.5 Economic Impacts
The mad honey trade can have significant economic impacts on local communities, particularly in rural and indigenous areas where it is produced. It provides income generation and employment opportunities, contributing to the economic development of these regions. Assessing the social and cultural significance of mad honey production is essential for understanding its broader impacts. Supporting sustainable business models that balance profitability with social and environmental responsibility is central to fostering long-term sustainability. This involves setting out fair compensation for local beekeepers, investing in community development, and promoting practices that protect local ecosystems.3.2.6 Future Outlook
The future outlook for the mad honey market involves monitoring trends and developments such as shifts in consumer preferences, emerging health trends, and technological advancements. These factors can influence demand and open new avenues for growth. Expanding into new markets or product categories, diversifying product offerings, and forming strategic partnerships can help businesses capitalize on growth opportunities. Embracing sustainability initiatives and responsible business practices is increasingly important as consumers and regulators place greater emphasis on environmental and social responsibility. Staying ahead of market expectations and regulatory changes allows businesses to adapt and thrive in the evolving mad honey market.

3.3 How Bees Help in the Sustainability of Mad Honey
The role of bees in the sustainability of mad honey production is multifaceted and integral. From their foraging and pollination activities to hive management practices and contributions to ecosystem services, bees are essential to maintaining the health and balance of the environment that supports mad honey production.3.3.1 Bee Foraging and Pollination
Bees are indispensable in the production of mad honey due to their foraging activities. They collect nectar from rhododendron flowers using their long proboscis, an intricate process that involves visiting numerous flowers. This foraging not only results in the collection of nectar, which is later converted into honey but also facilitates the pollination of rhododendron plants. Pollination is critical for the reproduction of these plants, ensuring their continued growth and the availability of nectar for future generations of bees. This symbiotic relationship supports biodiversity by helping maintain the population of the plants and other flora within the ecosystem.3.3.2 Hive Management Practices
Preservation of honey bee species during honey gathering is paramount to maintaining ecological balance. Sustainable honey-gathering practices are essential to maintain bee health and the continuity of honey production. Harvesters should prioritize the conservation of bee populations by avoiding overharvesting and minimizing disturbance to their natural habitats. It's vital to monitor bee colonies regularly, maintaining their health and taking preventive measures against potential threats like pests and diseases By promoting biodiversity and avoiding harmful chemicals, harvesters can protect bee populations and sustain honey production for future generations.3.3.3 Ecosystem Services
Bees contribute significantly to ecosystem health through their pollination services. By pollinating a wide range of plants, including wildflowers, fruits, and vegetables, bees support plant reproduction and biodiversity. This, in turn, makes the soil more fertile and helps maintain the structural integrity of ecosystems. Healthy bee populations also benefit other pollinators and organisms within the ecosystem, creating a resilient and robust environment. Bees' pollination services are integral to the production of many crops that humans rely on for food, demonstrating their importance beyond honey production.3.3.4 Challenges and Solutions
Despite their vital role, bee populations face numerous challenges that threaten their survival. Habitat loss due to urbanization and agricultural expansion reduces the availability of forage and nesting sites for bees. Pesticide exposure from conventional farming practices can weaken bees and make them more susceptible to diseases. Pathogens, such as the Varroa mite, and climate change further exacerbate these threats, leading to declining bee populations.
Addressing these challenges requires a multilayer approach. Implementing habitat conservation measures, for example, creating and preserving wildflower meadows, forests, and cliffsides, provides bees with the necessary resources to thrive. Reducing pesticide use and promoting bee-friendly agricultural practices, such as integrated pest management, can help mitigate the negative impacts of chemicals on bees. Additionally, research and development of disease-resistant bee strains and improved hive management techniques are essential for combating pathogens and ensuring the health of bee colonies.

Frequently Asked Questions
After learning everything about mad honey and its trade, you might have some questions. Here we have the answers to some of your most common questions.What is mad honey, and why is it called "mad"?
Mad honey is a unique type of honey produced by bees that collect nectar from rhododendron flowers, which contain grayanotoxins. These toxins can induce intoxication, often referred to as "madness," when consumed in large quantities, hence the name "mad honey."Where is mad honey produced, and how is it harvested?
Mad honey is primarily produced in regions where rhododendron flowers are abundant, such as Nepal, Turkey, and parts of the Himalayas. In some places, beekeepers place hives near the plants during the flowering season. Bees collect the nectar, which is then processed into honey. Harvesting involves collecting honeycomb frames from the hives or gathering them from the cliff sides where the bees live and extracting the honey.Is mad honey legal, and what are the regulatory concerns?
The legality of mad honey varies by region. In some countries, it is freely available, while in others, restrictions or regulations are in place due to its psychoactive properties. Regulatory concerns focus on providing consumer safety and preventing misuse. Authorities may impose labeling requirements, quality standards, and sale restrictions to mitigate health risks associated with grayanotoxin poisoning.
Mad honey, with its unique properties and rich cultural heritage, offers a fascinating glimpse into the traditions and ecosystems of Nepal and other regions. While its therapeutic benefits and distinctive taste attract global interest, the trade also presents significant challenges. Ethical considerations, environmental sustainability, and regulatory compliance are critical to making sure that the mad honey industry can thrive responsibly.
Consumers, traders, and policymakers alike have a role in preserving the delicate balance between tradition and commerce. By implementing the practices mentioned above, the mad honey trade can contribute positively to local economies and global health trends.
If you are looking to experience the unique flavor of mad honey, why not check Maddest Mad Honey? We work closely with Nepal's honey hunters to bring you the best, most potent mad honey. Our honey is sourced ethically, and we make sure harvesting is done responsibly to protect bees and their habitat. Plus, we have strict quality control measures to guarantee you only receive premium and pure mad honey.
Order your jar today and discover a world of richness and depth.